John J O Accarino MD, 1, Allison Ramsey MD, 2, Upeka Samarakoon PhD, MD3, Elizabeth Phillips MD, 4, Alexei Gonzalez-Estrada MD, 5, Iris M Otani MD, 6, Xiaoqing Fu MS, 3, Aleena Banerji MD, 1, Cosby A Stone Jr MD, MPH, 7, David A Khan MD, 8, Kimberly G Blumenthal MD, MSc, 9; United States Drug Allergy Registry Study Team
Affiliations
- Division of Rheumatology, Allergy, and Immunology, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts; Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
Rochester Regional Health, Rochester, New York; Department of Allergy/Immunology, University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester, New York.
Division of Rheumatology, Allergy and Immunology, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hosptial, Boston Massachusetts
- Division of Allergy, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee; Center for Drug Safety and Immunology, Department of Medicine, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee.
- Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Sleep Medicine, Department of Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Florida.
- Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, Allergy and Sleep Medicine, Department of Medicine, UCSF Medical Center, San Francisco, California.
- Division of Allergy, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee.
- Division of Allergy and Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas.
- Division of Rheumatology, Allergy, and Immunology, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts; Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts. Electronic address: kblumenthal@mgh.harvard.edu.
Publication Date
July 26, 2023
Full Text
PMID: 37557950
Abstract
Older adults have an increased risk of adverse drug reactions and negative effects associated with alternative antibiotic use. Although the number of antibiotic allergies reported increases with age, the characteristics and outcomes of older adults receiving drug allergy assessment are unknown.
To assess the characteristics and outcomes of drug allergy evaluations in older adults.
We considered patients aged above or equal to 65 years enrolled in the United States Drug Allergy Registry (USDAR), a US multisite prospective cohort (January 16, 2019 to February 28, 2022). Data were summarized using descriptive statistics
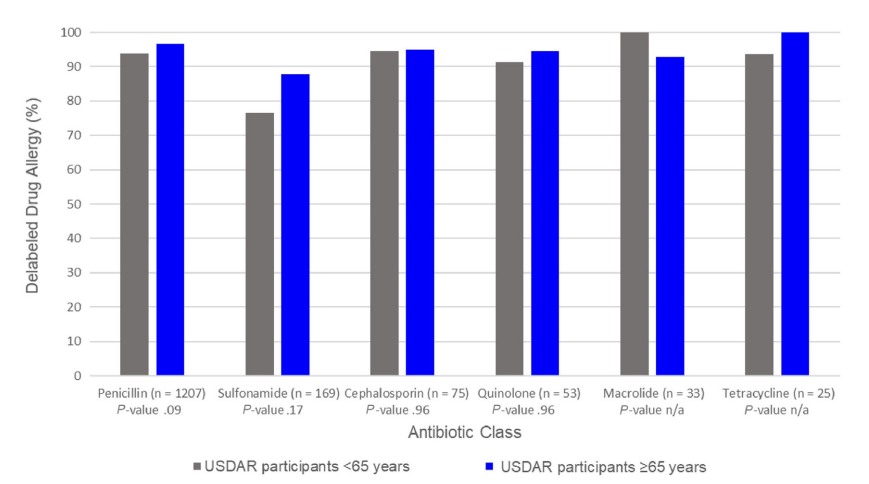
Of 1678 USDAR participants from 5 sites, 406 older adults aged above or equal to 65 years (37% 65- 69 years, 37% 70-74 years, 16% 75-79 years, and 10% ≥80 years) received 501 drug allergy assessments. USDAR older adults were primarily of female sex (69%), White (94%), and non-Hispanic (98%). Most USDAR older adults reported less than or equal to 1 infections per year (64%) and rated their general health as good, very good, or excellent (80%). Of 296 (59%) penicillin allergy assessments in USDAR older adults, 286 (97%) were disproved. Other drug allergy assessments included sulfonamide (n = 41, 88% disproved) and cephalosporin (n = 20, 95% disproved) antibiotics. All 41 drug allergy labels in USDAR participants aged above or equal to 80 years and all 80 penicillin allergy labels in USDAR men aged above or equal to 65 years were disproved.
Older adults represented a quarter of USDAR participants but were neither racially nor ethnically diverse and were generally healthy without considerable antibiotic need. Most older adults presented for antibiotic allergy assessments, the vast majority of which were disproved. Drug allergy assessments may be underutilized in the older adults who are most vulnerable to the harms of unconfirmed antibiotic allergy labels
Figure – Pareto chart of reported drug allergies in USDAR patients aged above or equal to 65 years
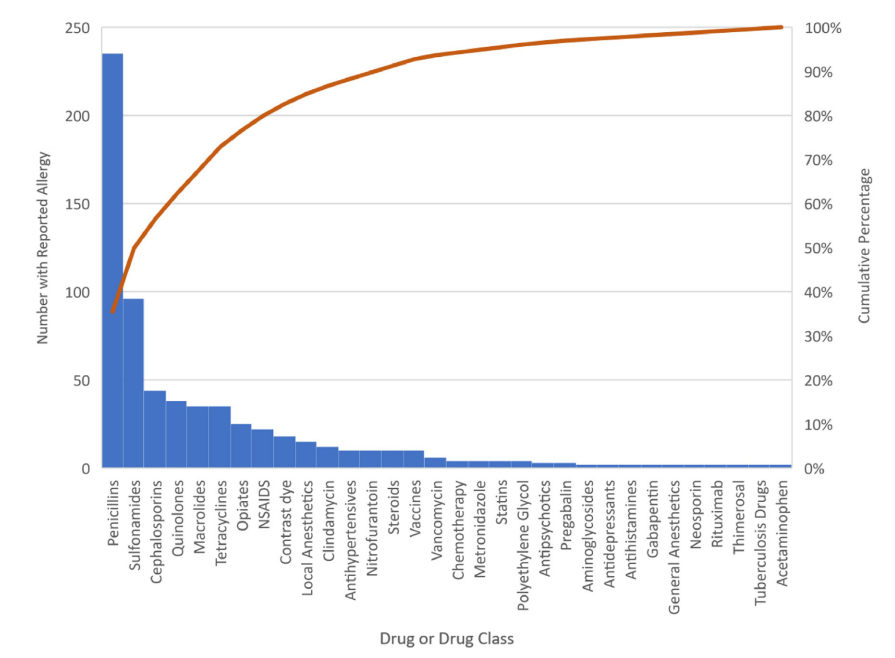
Pareto chart of reported drug allergies in USDAR patients aged above or equal to 65 years. Drugs reported by more than or equal to 2 patients are included.
Figure – Flow diagram of USDAR participants and drug evaluation outcomes. USDAR, United States Drug Allergy Registry.
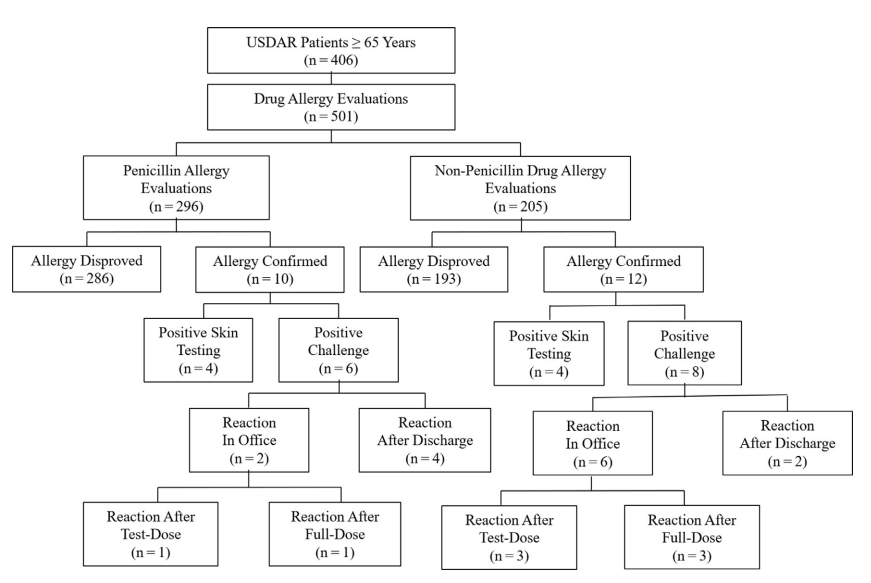
Figure – Rates of delabeled antibiotic allergy label by age. USDAR, United States Drug Allergy Registry.